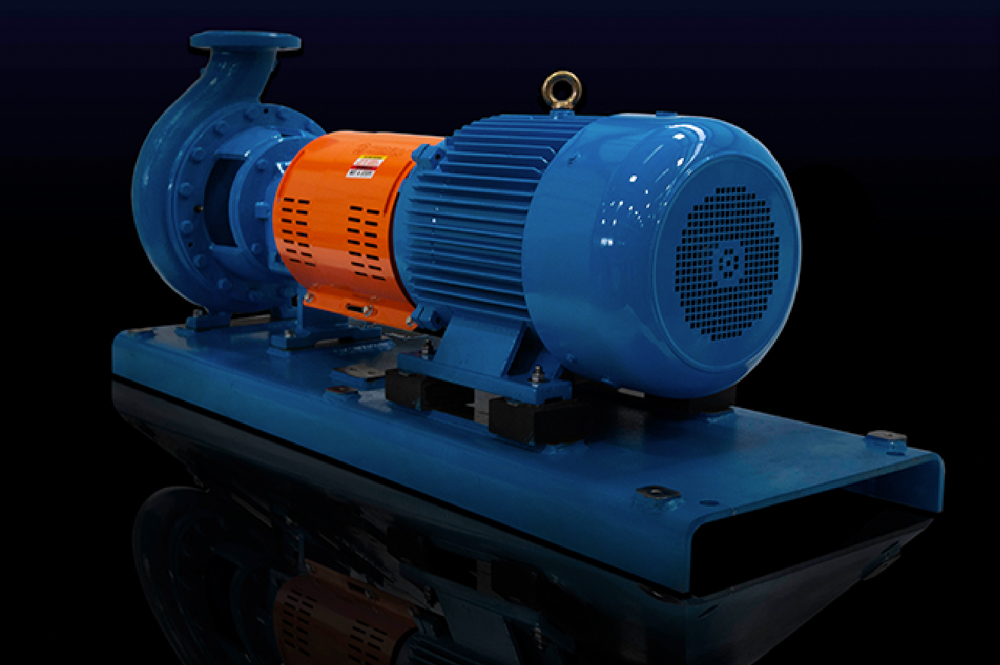
Understanding the components of a centrifugal pump is crucial for anyone involved in its operation, maintenance, or selection. Centrifugal pumps play a vital role in various industries, providing an efficient means of transferring liquids under pressure. However, to harness their full potential, one must grasp the intricacies of centrifugal pump parts, as they directly influence the pump's performance, reliability, and lifespan. Familiarity with these components not only aids in better operational efficiency but also minimizes the risk of malfunctions and costly downtime.
Each part of a centrifugal pump, from the impeller to the volute, serves a specific function that contributes to the overall system’s effectiveness. Understanding how these parts interact provides operators with insights into diagnosing issues, implementing effective maintenance strategies, and optimizing pump operation according to varying conditions. By exploring the essential elements of centrifugal pump parts, personnel can ensure that they are equipped to maintain high levels of productivity and safety, ultimately supporting the operational goals of their respective industries.

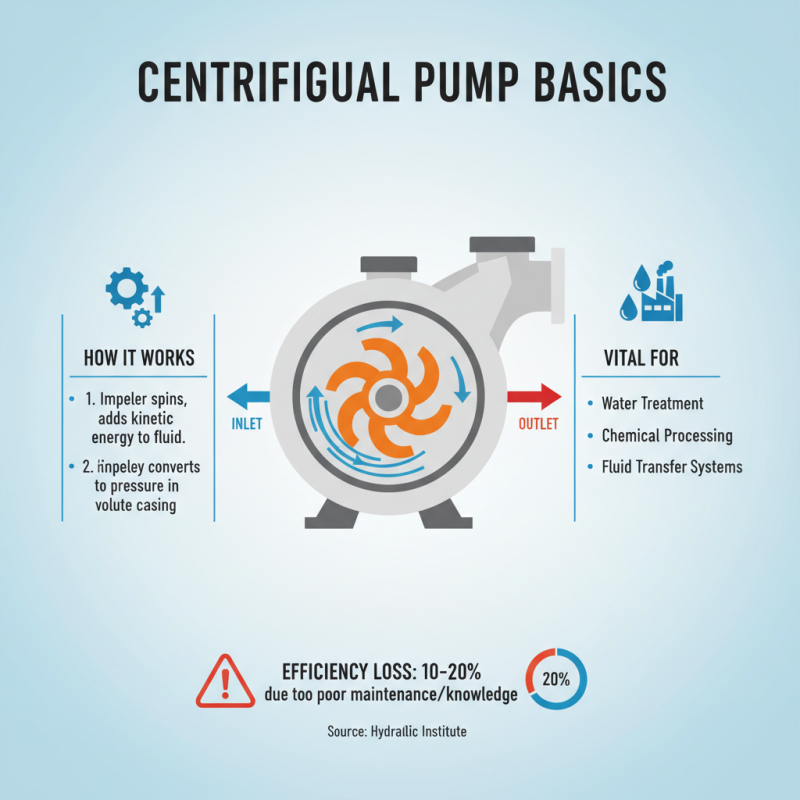
Centrifugal pumps are vital components in various industrial applications, serving as the backbone of fluid transfer systems. Understanding the basics of how these pumps work is essential for ensuring efficient operation. At the core of a centrifugal pump is its impeller, which rotates to impart kinetic energy to the fluid, converting it into pressure energy as it moves through the volute casing. This process enables the pump to maintain a steady flow of liquid, which is critical in sectors ranging from water treatment to chemical processing. According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, improper maintenance and a lack of knowledge about pump components can lead to a staggering 10-20% reduction in efficiency, underscoring the importance of a solid understanding of pump mechanics.
Maintaining optimal performance requires more than just awareness—it involves actively engaging with the pump's various parts, such as bearings, seals, and the motor. Regular inspections and replacements can prevent unexpected downtime, which can be costly to operations. For instance, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers notes that well-maintained pumps can operate at efficiencies above 85%, while poorly maintained systems often dip below 60%.
**Tips:** One effective way to educate your team is by providing training sessions focused on pump maintenance and troubleshooting. Additionally, consider creating a checklist for routine inspections to ensure every critical part is assessed regularly. This proactive approach not only extends the lifespan of your centrifugal pumps but also enhances overall system reliability.
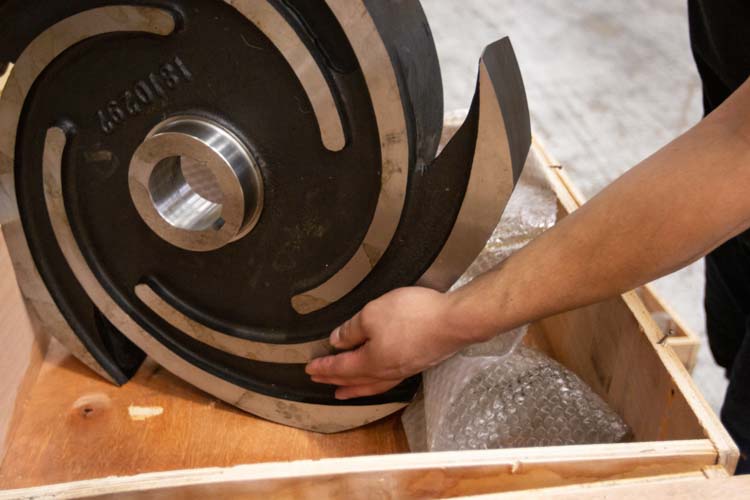
Understanding the key components of centrifugal pumps is crucial for ensuring their efficient operation in various industries. At the heart of a centrifugal pump lies the impeller, which converts mechanical energy into kinetic energy, allowing fluid to flow. According to the Hydraulic Institute, the impeller's design significantly impacts performance characteristics such as flow rate and pressure head. A well-optimized impeller can reduce energy consumption by up to 20%, making it a vital element in pump efficiency.
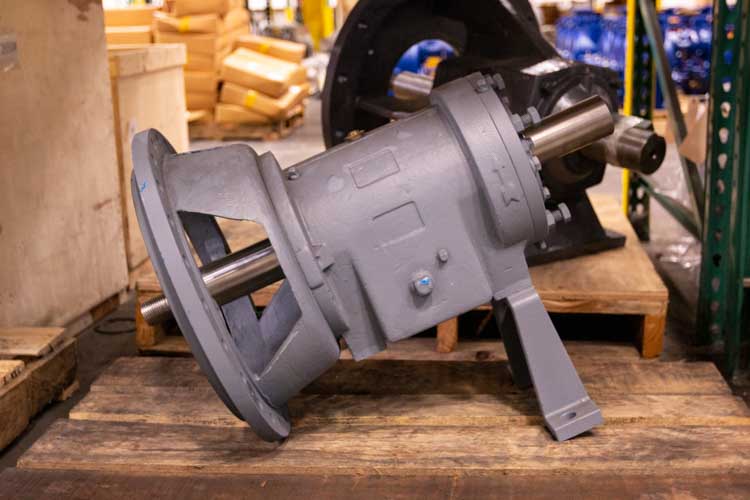
Another essential component is the pump casing, which houses the impeller and helps to guide the fluid in a controlled manner. The casing not only supports the impeller but also helps to convert the fluid's kinetic energy into pressure energy as it exits the pump. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, improper casing design can lead to turbulence and energy loss, reducing the pump's overall efficiency by as much as 15%. Additionally, the wear ring's role should not be overlooked, as it minimizes leakage and maintains efficiency throughout the pump's operational life. Understanding these components allows operators to perform necessary maintenance and upgrades, ensuring optimal pump operation and longevity.

Proper maintenance is vital for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of centrifugal pumps. These pumps are widely used in various industries due to their ability to move fluids effectively. However, neglecting their maintenance can lead to performance issues, including reduced flow rates and increased energy consumption. Regular inspections and servicing help identify potential problems before they escalate, ensuring that the pump operates at peak efficiency and minimizes downtime.
Key maintenance practices include monitoring the condition of critical components such as the impeller, seals, and bearings. Regularly checking for wear and tear can prevent costly repairs and interruptions in operation. Additionally, maintaining proper lubrication and ensuring that the pump is free from debris can significantly enhance its performance. By investing time and resources into maintaining centrifugal pumps, operators not only extend the life of the equipment but also optimize their operational costs and energy efficiency.
Centrifugal pumps are pivotal in various industries, yet their performance can be hindered by a range of common issues. One prevalent problem is cavitation, which occurs when the pressure in the pump inlet drops below the vapor pressure of the liquid. This can lead to severe damage over time. To prevent cavitation, ensure that the pump operates within the specified NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head) requirements and maintain adequate fluid levels in the supply tank.
Another issue that can affect centifugal pump efficiency is wear and tear on the impeller and casing, leading to decreased performance and increased energy consumption. Regular inspections and maintenance are critical to address wear before it escalates. Replacing worn parts promptly can help maintain the pump’s efficiency and prolong its lifespan.
**Tips:** Always monitor the pump for unusual vibrations or noises, which can be early signs of mechanical issues. Additionally, maintain a log of operational parameters to help identify patterns and rectify problems before they become significant issues. By understanding these common problems and implementing preventive actions, you can significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of your centrifugal pump system.
| Component | Function | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impeller | Creates flow and pressure in the pump | Wear and tear, clogging | Inspect regularly; clean to remove debris |
| Volute | Converts kinetic energy into pressure | Cavitation, corrosion | Monitor pressure; inspect for damage |
| Suction Pipe | Delivers fluid to the pump | Air leaks, blockage | Check for tight seals; clear obstructions |
| Discharge Pipe | Carries pumped fluid away | Pressure loss, leaks | Inspect for leaks; check pipe size |
| Bearings | Support the rotating shaft | Wear, overheating | Ensure proper lubrication; replace if damaged |
Selecting the right centrifugal pump is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring longevity in performance. According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, improper pump selection can lead to efficiency losses of up to 20-30%, which directly translates into increased operational costs. When assessing your needs, consider factors such as flow rate, head pressure, and the specific characteristics of the fluid being pumped. The right pump must also match the environmental conditions and the intended application to minimize wear and tear.
In addition to the technical specifications, understanding the specific materials and design of the pump can significantly impact its performance. A study published in the International Journal of Pump Engineering highlights that pumps made from corrosion-resistant materials can extend the lifespan of the equipment, especially in harsh applications where the fluid may contain abrasives or corrosive elements. By aligning pump characteristics with your operating environment and application requirements—such as viscosity, temperature, and chemical compatibility—you can greatly enhance the effectiveness and reliability of your pumping system, ultimately leading to substantial cost savings and improved operational success.