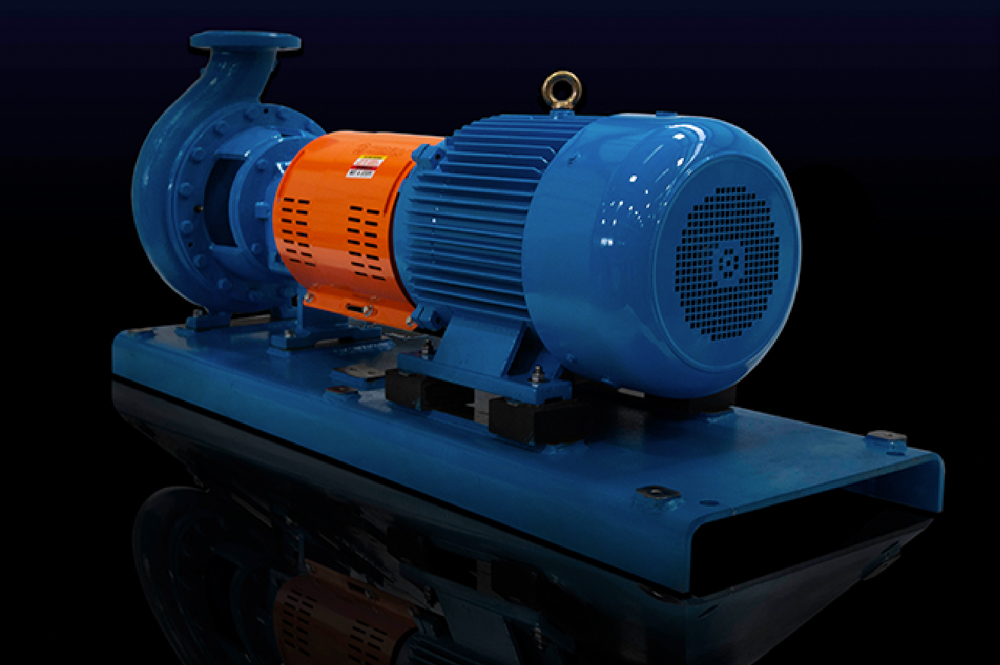

Understanding centrifugal pump parts is crucial for effective maintenance and operation. These pumps are widely used in various industries. They play a vital role in moving fluids efficiently. Knowing the components helps in troubleshooting issues.
Centrifugal pumps have several key parts. The impeller is essential; it adds energy to the fluid. The casing encloses the impeller, directing the flow. Seals prevent leaks, which can be a common issue. Regular inspection of these parts is necessary for optimal performance.
Yet, not everyone pays attention to these details. Ignoring worn or damaged parts can lead to failure. It's important to reflect on how often we check our equipment. Understanding centrifugal pump parts can save time and costs. Making this knowledge a priority is often overlooked.

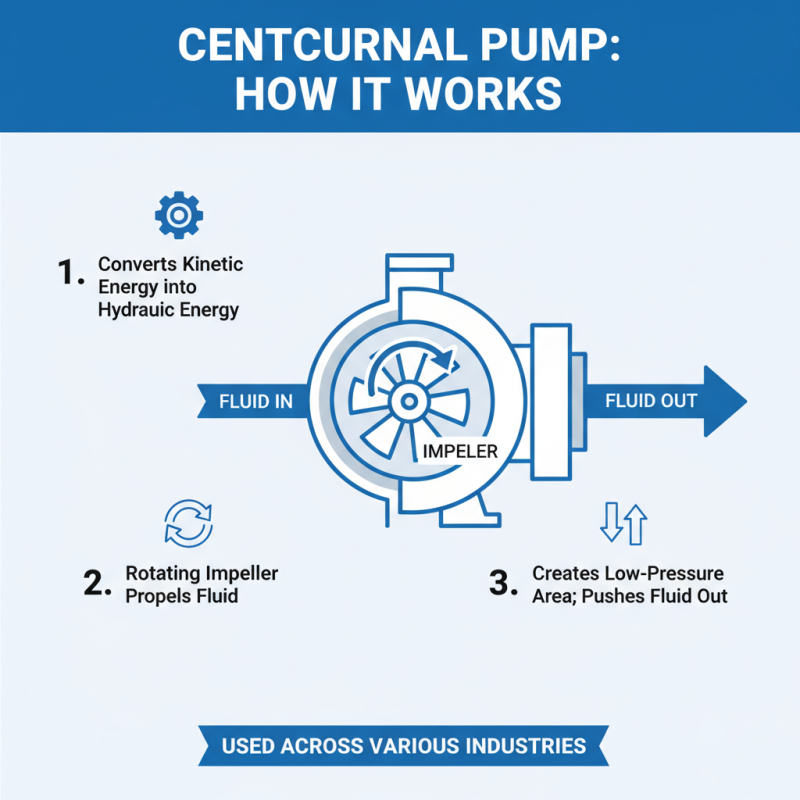
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in various industries. Their design revolves around converting kinetic energy into hydraulic energy. This process relies on a rotating impeller to propel fluid. The impeller spins rapidly, creating a low-pressure area. Fluid flows into the pump and is pushed out through the discharge.
According to research, centrifugal pumps account for about 80% of the total pump market. They excel in handling large volumes of liquids. However, many users overlook the importance of maintaining their components. Key parts include the impeller, casing, seals, and bearings. Each part plays a crucial role in the pump's efficiency. If one component fails, it can lead to significant downtime.
Professional studies suggest that proper identification of these parts can enhance operational efficiency. Inadequately maintained pumps can lead to energy losses. These losses often range between 5% to 10%. On the other hand, knowing common issues with seals or bearings can lead to timely repairs. Awareness can prevent costly breakdowns. Keeping these details in mind is essential for effective pump management.
Centrifugal pumps consist of several key components that work together to move fluids effectively.
The impeller is crucial. It spins rapidly, imparting energy to the fluid.
A well-designed impeller can significantly improve pump efficiency. However, not all impellers perform the same in various conditions.
Another major part is the volute, which collects the fluid from the impeller and directs it toward the discharge pipe.
The shape of the volute affects flow characteristics. A poorly designed volute can reduce pressure and flow. The casing, housing all these components, must be sturdy yet light.
Additionally, bearing and shaft play vital roles in pump operation.
Bearings reduce friction and wear, while the shaft transmits power from the motor to the impeller. When components are mismatched, the pump may vibrate excessively.
This can lead to premature failure.
Understanding these parts helps troubleshoot issues efficiently. Knowing where to look can make a significant difference in pump maintenance.
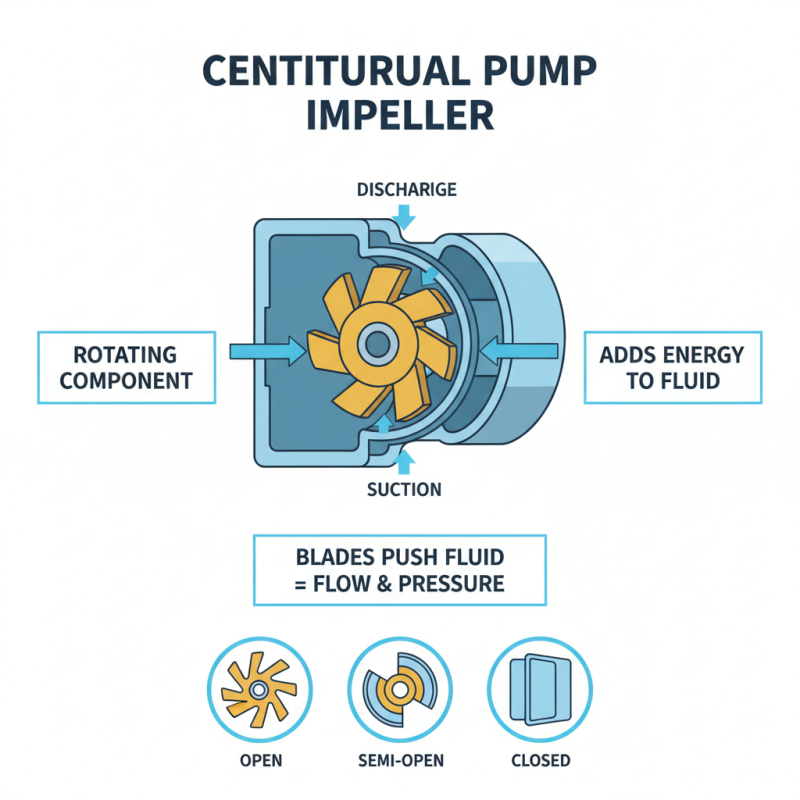
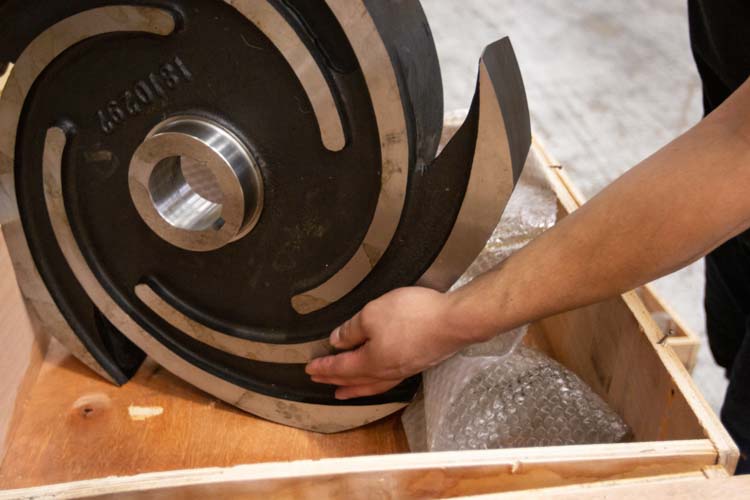
Understanding the impeller is crucial for identifying common centrifugal pump parts. The impeller is a rotating component that imparts energy to the fluid. Its design features blades that push fluid outward, creating flow and pressure. Different types of impellers exist, each serving a specific function based on application.
When observing an impeller, notice its size and blade shape. A larger impeller moves more fluid quickly, while smaller impellers are generally used for high pressure. The angle of the blades also plays a pivotal role in the efficiency of the pump. If blades are worn or damaged, performance may drop significantly. Inefficient impeller design can lead to cavitation, which damages the pump.
Not all pumps have identical impellers. Some may look visually appealing but perform poorly in practice. It’s vital to inspect the impeller regularly. Learning to spot wear and tear can save time and costs. Often, it’s easy to overlook minor signs of damage. Taking a closer look at the impeller can prevent future problems. Be proactive; this can lead to better pump operation and longevity.
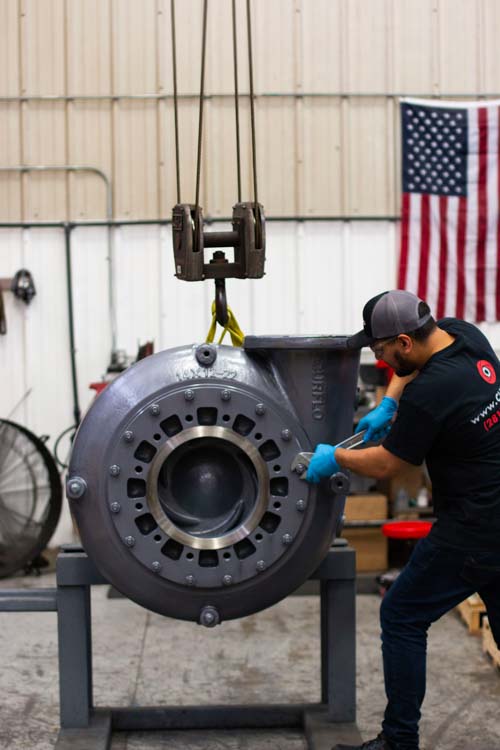
The casing of a centrifugal pump plays a crucial role in its overall efficiency. It encases the impeller, guiding the fluid directly to the discharge port. A well-designed casing minimizes turbulence, which can lead to energy loss. When flow enters the pump, the shape of the casing helps maintain smooth movement. Any deviation in its design can cause inefficiencies.
Casing materials also impact pump performance. A sturdy casing can withstand high pressure and protect internal components. However, using the wrong material can lead to corrosion or wear over time. Regular inspections are essential. Small cracks or erosion can drastically reduce the pump's lifespan. Addressing these issues early can save time and money.
Understanding the relationship between the casing and pump efficiency is vital. An unintended misalignment can create vibrations. Excessive vibration not only wears out the pump but can destabilize the entire system. Identifying these problems early is key to maintaining optimal performance. The casing might seem simple, but its design and condition are not to be overlooked.
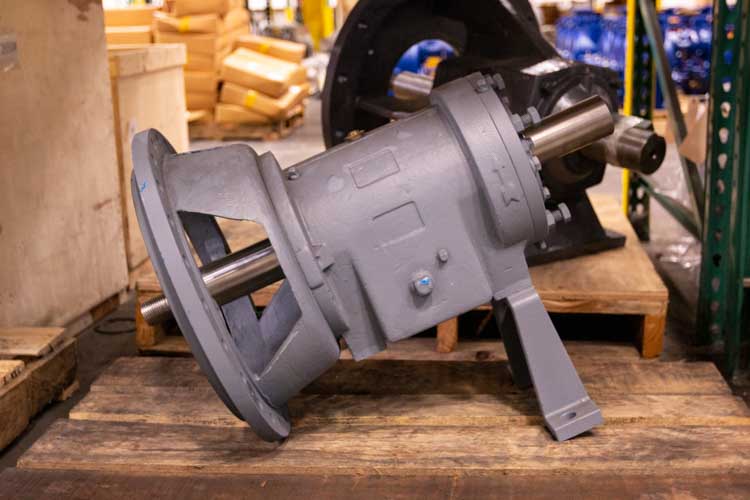
The pump shaft plays a critical role in centrifugal pumps. It transmits power from the motor to the impeller. A well-constructed shaft minimizes vibrations and ensures smooth operation. Typical shaft materials include stainless steel and carbon steel, providing durability and corrosion resistance. However, wear and tear can happen. Regular inspections are necessary to assess for bends or cracks, which can compromise efficiency.
The mechanical seal serves as another vital part of centrifugal pumps. It prevents fluid leakage along the shaft. A good seal ensures reduced maintenance costs and extends pump life. Reports indicate that 40% of pump failures are linked to seal issues. It's essential to monitor seal integrity regularly. Factors like operating temperature and pressure can affect seal performance. Ignoring these details may lead to costly downtime.
Both the pump shaft and mechanical seal require attention. Addressing minor issues early can prevent major failures later. Observing the condition of these components can enhance overall pump reliability. Maintenance reports highlight that proactive measures save time and resources in the long run.



















