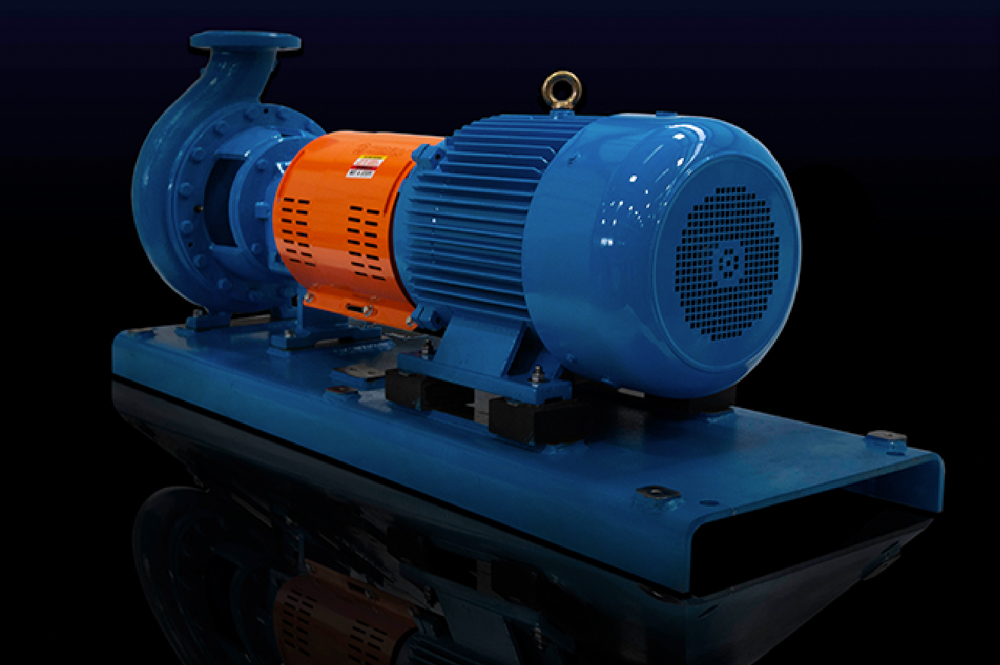

In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial machinery, the selection of the right self priming centrifugal pump has become a critical consideration for engineers and operators alike. According to a recent market research report by Grand View Research, the global centrifugal pump market was valued at approximately USD 33.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand significantly over the coming years. This growth underscores the increasing demand for reliable pumping solutions across various sectors, including water and wastewater management, chemical processing, and agriculture.
Self priming centrifugal pumps are particularly notable for their ability to efficiently handle fluids while eliminating the need for manual priming, making them an optimal choice in situations where the pump's location may cause challenges in maintaining prime. With key advantages such as reduced downtime, simple operation, and adaptability to different fluid types, these pumps play an essential role in enhancing operational efficiency. However, selecting the appropriate self priming centrifugal pump involves careful consideration of factors such as flow rate, application-specific requirements, and environmental conditions, ensuring that the right pump meets the unique needs of your operation.

Self-priming centrifugal pumps are highly efficient and versatile, making them ideal for various applications, from agricultural irrigation to industrial processes. The primary advantage of these pumps is their ability to draw liquid into the pump without needing to be manually primed. This feature is particularly beneficial in scenarios where the liquid source is located below the pump’s level, as it reduces the need for additional equipment and labor.
When selecting a self-priming centrifugal pump, consider the specific application requirements. Factors such as flow rate, total dynamic head, and the nature of the fluid being pumped (e.g., viscosity, temperature, and chemical composition) play crucial roles in determining the right pump. Additionally, ensure that the pump can handle any solids or debris in the fluid to avoid clogging and potential damage.
**Tips:** Always consult the pump's performance curves to match your operational needs accurately. Regular maintenance checks are essential to ensure efficient operation over time. Keep the pump and surrounding area clean to prevent debris interference, which can affect the self-priming capabilities. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision that meets your application needs effectively.
When selecting a self-priming centrifugal pump, there are several key factors to consider that can significantly impact its effectiveness and efficiency for your specific application. Firstly, the pump's flow rate is crucial; it should match the demands of the system, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM). Reports from the Hydraulic Institute indicate that pumps operated within 10% of their best efficiency point (BEP) show a 20% increase in energy efficiency compared to those that do not. Therefore, understanding your required flow rate is essential for maximizing performance.
Another critical aspect is the total dynamic head (TDH), which combines static lift, friction losses, and pressure requirements in the system. A comprehensive analysis of these parameters ensures that the pump can handle the operational demands without overworking, which could lead to premature failure. Industry standards suggest that exceeding the TDH by more than 20% can reduce pump lifespan and efficiency significantly.
**Tips:** Always consider the materials used in the pump construction, especially if you're dealing with corrosive fluids or high temperatures. Selecting the right material can prevent costly replacements and downtime. Additionally, evaluate the pump’s priming capability by checking its net positive suction head required (NPSHr) against the available NPSH in your system. Proper alignment of these factors will optimize the pump's performance and longevity.
When selecting a self-priming centrifugal pump, understanding the flow rate and head requirements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. The flow rate, usually measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), indicates the volume of fluid the pump can move within a specific time frame. Assessing your specific application’s flow demands helps in determining the correct pump size. For scenarios that require continuous operation, it's essential to establish both the average and peak flow rates, as this information influences the selection of a pump capable of meeting those needs consistently.
Equally important is the head requirement, which refers to the height the fluid must be lifted or the pressure required to move it through the system. This is typically measured in feet or meters. Understanding the total dynamic head (TDH), which incorporates the static lift, friction losses, and any additional pressure drops, plays a vital role in pump selection. By accurately calculating the TDH, users can choose a pump that will not only handle the required flow but also overcome any resistance in the piping system. This careful assessment of flow rate and head ensures efficiency, reliability, and longevity in pump operation.
| Pump Type | Max Flow Rate (GPM) | Max Head (Feet) | Power Requirement (HP) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self Priming Centrifugal Pump A | 100 | 40 | 2 | Irrigation |
| Self Priming Centrifugal Pump B | 150 | 30 | 3 | Water Transfer |
| Self Priming Centrifugal Pump C | 80 | 50 | 1.5 | Chemical Processing |
| Self Priming Centrifugal Pump D | 200 | 20 | 4 | Sewage |
| Self Priming Centrifugal Pump E | 120 | 25 | 2.5 | Construction |

When selecting a self-priming centrifugal pump, material compatibility and durability are critical factors that directly influence the pump's performance and longevity. According to a recent report by the Hydraulic Institute, nearly 30% of pump failures can be attributed to inadequate material selection, highlighting the importance of understanding the properties of various materials used in pump construction. Pumps often operate in harsh environments, which can lead to premature wear or chemical degradation if the materials are not appropriately chosen. For instance, stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance for water and mild chemicals, while materials like polypropylene are ideal for acidic solutions.
Durability is not just about the material’s resistance to the working environment; it also involves the physical properties of the materials under operational stress. A study from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers emphasized that the tensile strength and fatigue limits of the pump materials need to match the demands of the application. For example, pumps used in mining or heavy industrial applications often require high-strength alloys to withstand abrasive particles. Understanding these parameters and how they relate to specific applications ensures that the chosen pump will maintain reliability over time and reduce maintenance costs, further reinforcing the necessity of careful material evaluation in pump selection.
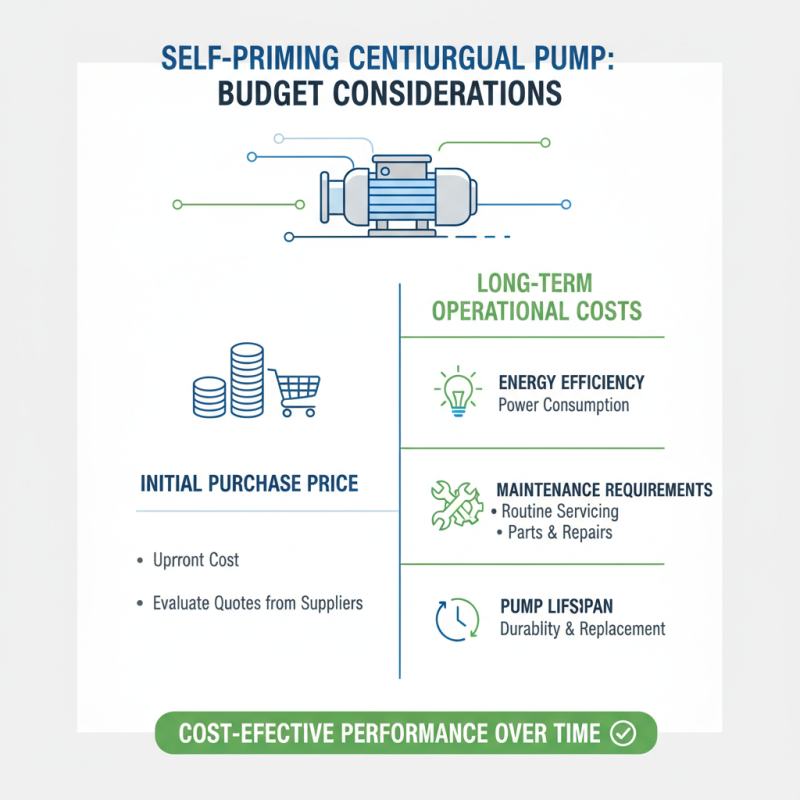
When selecting a self-priming centrifugal pump, budget considerations play a crucial role in the decision-making process. The initial purchase price of the pump is often the first thing to evaluate, but it is equally important to consider the long-term operational costs. Factors such as energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, and the lifespan of the pump can substantially affect overall expenditures. Therefore, it's prudent to look for pumps that not only fit your budget but also deliver cost-effective performance over time.
Moreover, various types of self-priming centrifugal pumps exist, each with different price points and efficiencies. While it might be tempting to choose the least expensive option, investing in a pump with better durability and energy efficiency can lead to lower operational costs in the long run. For instance, some pumps might offer advanced features that ensure reliable operation and reduced energy consumption, which can translate into significant savings. Evaluating the total cost of ownership—factoring in purchase price, maintenance, and energy costs—will help you choose the pump that truly meets your needs without breaking the bank.



















